
A hybrid inverter system sits at the core of modern energy storage architecture, acting as the control center that coordinates solar generation, battery storage, grid interaction, and on-site loads. In commercial and industrial (C&I) projects, hybrid inverters are deployed to optimize self-consumption, manage peak demand, ensure power quality, and provide backup power for mission-critical operations.
As energy storage deployments scale across different use cases, system designers must address a fundamental electrical distinction: three-phase versus split-phase power architecture. This distinction directly influences inverter selection, system topology, scalability, and long-term operational flexibility. Understanding how hybrid inverter systems adapt to these two power formats is therefore essential for C&I developers.

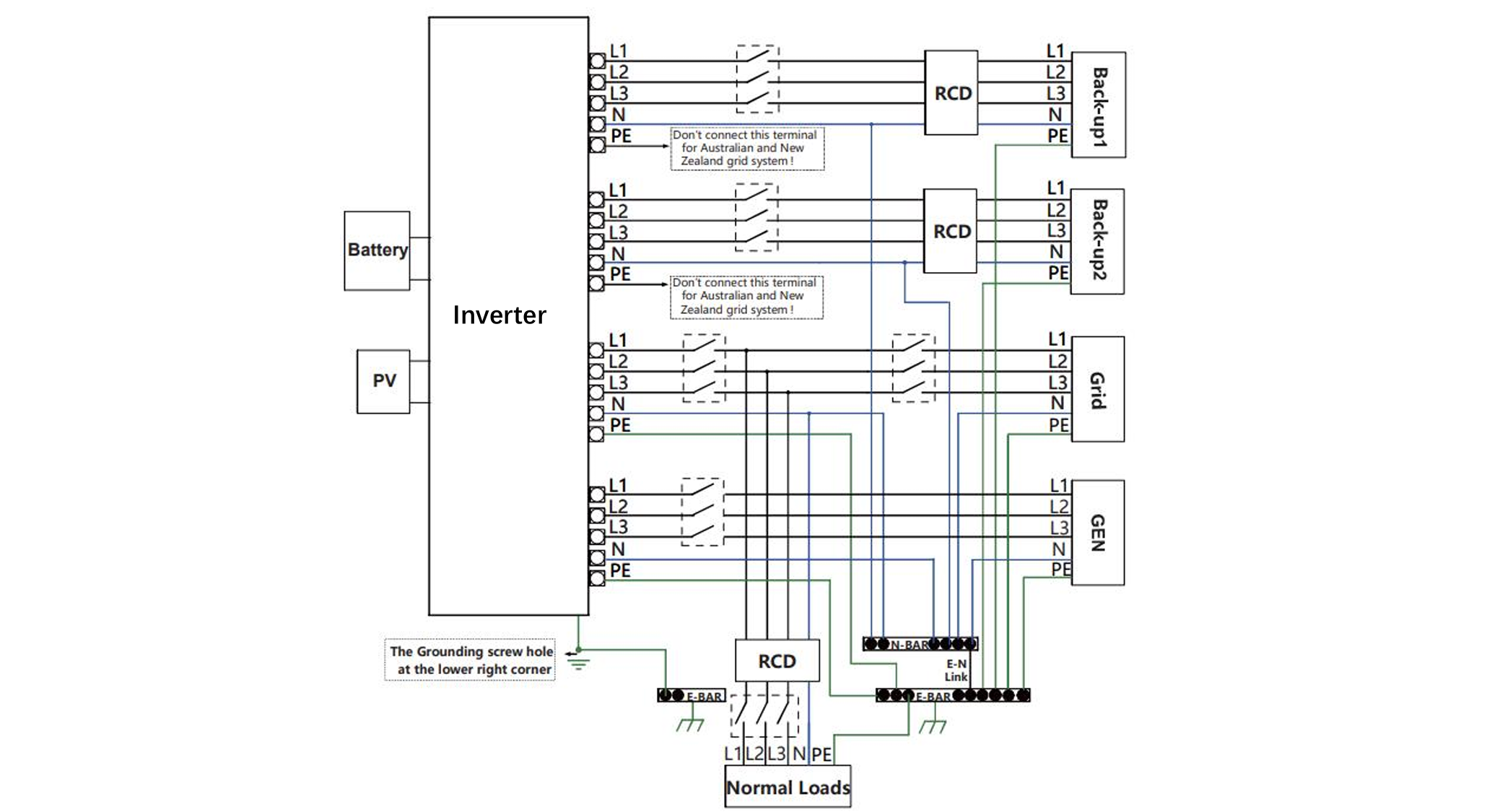
A hybrid inverter integrates multiple functions into a single platform: it converts DC power from solar PV and batteries into AC power, manages battery charging and discharging, coordinates grid interaction, and executes energy management logic. Unlike traditional string inverters or standalone battery inverters, a hybrid inverter system reduces component complexity while improving system efficiency and controllability.
The key differences between three-phase and split-phase hybrid inverter systems stem from their electrical structure and intended application scale:
l Three-phase hybrid inverter systems distribute power across three alternating currents, offset by 120 electrical degrees. This configuration delivers higher power density, smoother load distribution, and improved efficiency for large loads. As a result, three-phase systems are standard in factories, commercial buildings, data centers, and large-scale energy storage projects.
l Split-phase hybrid inverter systems, commonly operating at 120/240V, divide power into two opposing phases. This architecture aligns with residential electrical standards in many markets and is well suited for homes, small businesses, and light commercial installations where loads are moderate, but flexibility and backup capability remain critical.
While both types perform the same core hybrid functions, their design priorities—capacity, scalability, and load handling—differ significantly.
C&I energy storage projects typically operate in complex electrical environments where high peak demand, fluctuating and unbalanced loads, strict uptime requirements, and long-term scalability must all be addressed simultaneously. Facilities such as factories, commercial buildings, and logistics centers often experience sharp load variations driven by production cycles, HVAC systems, and high-power equipment. In addition, project owners increasingly expect energy storage systems to deliver multiple value streams—such as peak shaving, backup power, self-consumption optimization, and grid interaction—while remaining compliant with grid codes and minimizing total cost of ownership. These requirements place significant demands on the inverter system, making architectural flexibility and operational stability critical design considerations.[TW1]
Three-phase hybrid inverter systems are inherently well suited to these challenges due to their ability to handle high power levels and balanced load distribution. By spreading electrical load across three phases, these systems reduce current stress, improve efficiency, and maintain voltage stability under dynamic operating conditions. Three-phase architectures also support parallel operation and modular expansion, allowing C&I projects to scale from tens of kilowatts to megawatt-level installations without redesigning the core system. This makes them particularly effective for applications such as peak demand management, continuous industrial operation, and integration with advanced energy management systems.
Split-phase hybrid inverter systems, while more commonly associated with residential applications, can still play a meaningful role in small commercial or light C&I scenarios where power demand is moderate and electrical infrastructure follows residential standards. Their simpler wiring requirements, compatibility with 120/240V systems, and lower initial investment make them suitable for small offices, retail spaces, mixed-use buildings, or distributed energy storage deployments. In these contexts, split-phase systems provide reliable backup power, support solar self-consumption, and offer a practical balance between performance and cost, even though they are not intended for heavy industrial loads.
Having explored the distinct technical roles and application contexts of three-phase and split-phase hybrid inverters, the conversation now shifts to a practical example of a three-phase hybrid solution that exemplifies the capabilities needed in both commercial & industrial and advanced residential energy storage projects. One strong solution in today’s market is the Megarevo H3 Hybrid Three‑Phase Inverter.
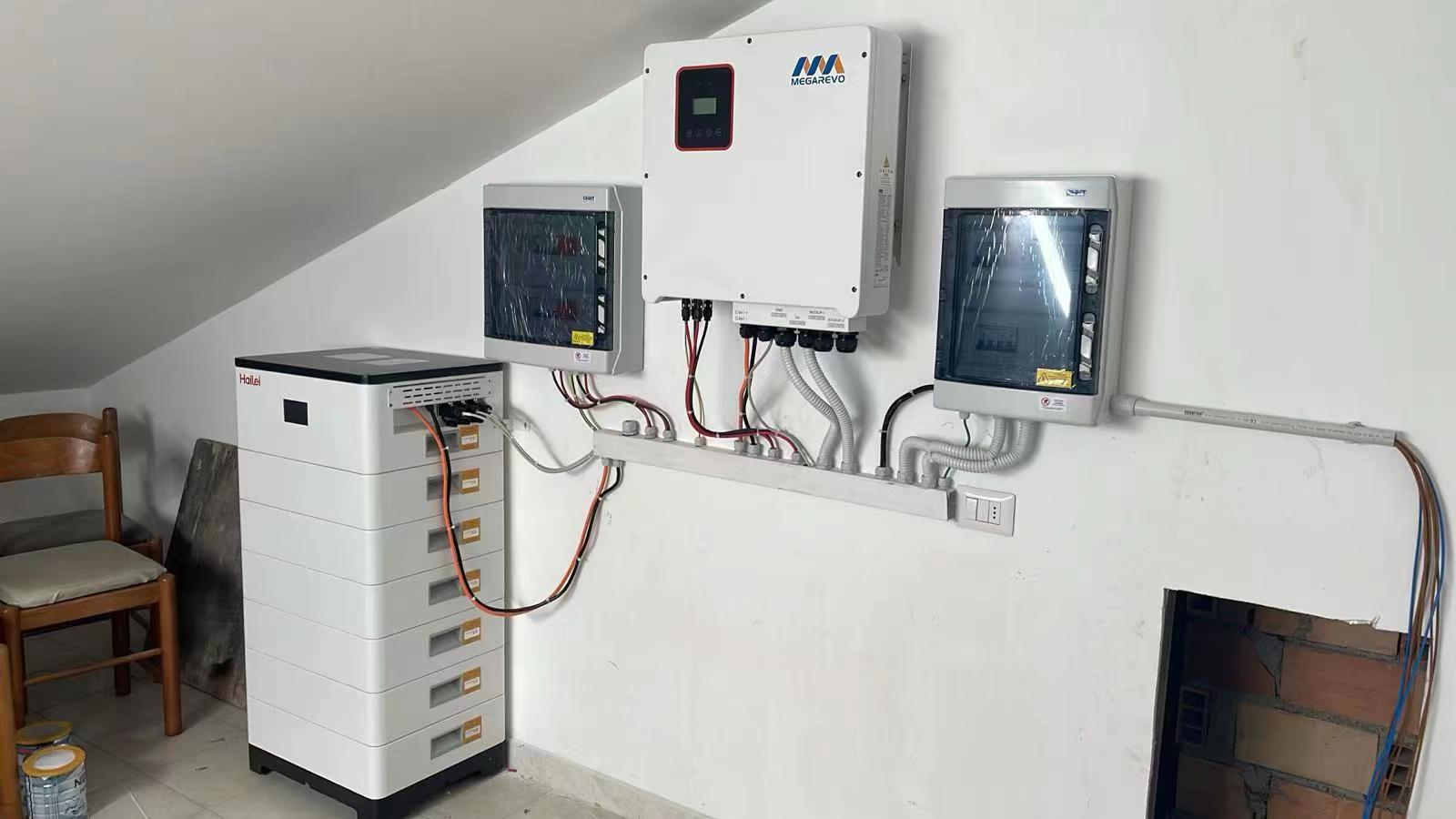

Our three-phase hybrid inverter portfolio supports simultaneous connection of PV arrays, battery storage, grid interface, and critical loads, providing the foundational integration needed for modern energy management strategies. The H3 Series models offer multiple MPPT (maximum power point tracking) inputs, enabling optimized solar energy harvest even in varied irradiance conditions, and are capable of handling 100 percent unbalanced loads, which is crucial for real-world three-phase systems where load distribution may not be perfectly symmetrical. With maximum conversion efficiencies approaching 97.9%, these inverters strike a balance between high performance and economical operation.
Safety and compliance are embedded into the product design: Megarevo’s three-phase hybrid inverters are certified to international standards (IEC/EN 62109-1/-2 for safety and EN50549-1, VDE4105, and G99 for grid connection), ensuring adherence to rigorous electrical and grid-integration protocols across global markets. This certification suite supports deployment in regulated environments where grid compliance is a prerequisite.
From a functional standpoint, these inverters also support black start capability—the ability to energize loads from battery or PV without grid presence—which enhances resilience in outage scenarios, making them suitable for facilities requiring continuous power. Remote monitoring and 24/7 service support facilitate system oversight and reduce maintenance intervention, which is especially valuable in distributed C&I installations where uptime is a priority.
Conclusion
Hybrid inverter systems are central to achieving flexibility and reliability in modern energy storage, with three-phase and split-phase architectures addressing clearly different application needs. For C&I projects in particular, three-phase hybrid inverters provide the scalability, load-handling capability, and grid interaction required for complex operating environments.
Within this space, Megarevo’s capability lies in its focused expertise in hybrid inverter technology, offering standardized and customized solutions for residential, C&I, and microgrid applications, supported by global certifications, ODM services, and international delivery experience. This combination enables project developers to deploy energy storage systems that are not only technically aligned, but also scalable and future-ready.